Brilio.net - Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, internal organs and immune system. This disease attacks the body and can cause inflammation and tissue damage in various organs. One of the main dangers of lupus is that its symptoms can appear and disappear suddenly , making it difficult to recognize and treat appropriately.
The World Health Organization (WHO) notes that the number of lupus sufferers in the world currently reaches five million people, and every year more than 100 thousand new cases are found. Reporting from kemkes.go.id, according to 2016 Online Hospital Information System (SIRS) data, there were 2,166 inpatients diagnosed with lupus. These cases continue to double compared to 2014.
The high death rate due to lupus needs special attention because 25% or around 550 people died from lupus in 2016. Most lupus sufferers are women in the productive age group (15-50 years). However, lupus can also attack men, children and teenagers. Therefore, it is important to increase the awareness of lupus in the community to prevent the disease from spreading more widely.
Outreach helps increase public awareness about lupus, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and management. With increased understanding of lupus among the general public, individuals who may be experiencing symptoms can recognize early signs of the disease and seek medical help more quickly.
So that you don't make the wrong move, check out brilio.net's complete review of the meaning of lupus, its causes, symptoms and how to deal with it, as reported by various sources on Thursday (16/5).
Causes of lupus

photo: freepik.com
There are several things that trigger lupus. Researchers and medical experts believe that lupus is caused by a combination of genetic, environmental and immunological factors. There are several factors that trigger lupus as follows.
1. Genetic factors
There is evidence to suggest that genetic factors play a role in the development of lupus. Individuals who have a family history of lupus have a higher risk of developing the disease. However, lupus is not directly inherited like other genetic diseases, but there are genetic predispositions that can increase a person's risk of developing lupus.
2. Environmental factors
Various environmental factors have been linked to the development of lupus, such as sun exposure, certain viral infections, exposure to cigarette smoke, and exposure to certain chemicals. Exposure to this environment can trigger an autoimmune response in susceptible individuals, causing inflammation and tissue damage.
3. Immunological factors
Lupus is an autoimmune disease, which means the body's immune system attacks the body's own healthy tissue. An imbalance or disturbance in the immune system causes the production of antibodies that attack healthy tissue, such as skin, joints and other body organs. The condition can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, but the exact mechanisms are still not fully understood.
Symptoms of lupus

photo: freepik.com
Lupus has varying symptoms and can affect various parts of the body. Lupus symptoms can appear suddenly or develop gradually. The symptoms of lupus are as follows:
1. Excessive tiredness
Uncontrollable and persistent fatigue is a common symptom of lupus, even after adequate rest.
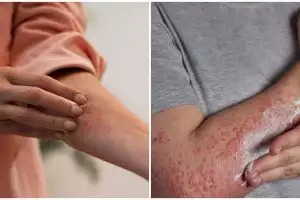
2. Skin rash
Skin rashes are one of the most common symptoms of lupus, usually occurring on the face (butterfly rash) and areas of skin exposed to sunlight.
3. Joint pain
Lupus often causes pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints, similar to the symptoms of arthritis.
4. Fever
Mild to moderate fevers are common in lupus patients, especially during lupus attacks.
5. Headache
A headache or dizziness is a common symptom of lupus.
6. Chest pain
Lupus can cause chest pain related to inflammation of the heart or lungs.
7. Kidney disorders
Kidney symptoms may appear in the form of increased blood pressure, swelling of the feet and hands, or changes in urine color.
8. Hematological disorders
Lupus can affect the blood, causing anemia, an increased risk of blood clots, or a decrease in the number of white blood cells or platelets.
9. Neurological disorders
Some lupus patients experience neurological disorders such as confusion, memory problems, or migraine headaches.
10. Mental and emotional disorders
Depression, anxiety, or sudden changes in mood may also occur in lupus patients.
How to treat lupus
photo: freepik.com
Managing lupus is a complex challenge, but with the right approach, many people can manage this condition. There are several things that can be used as references to treat lupus as follows:
1. Medicines
Your doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, or immunosuppressant drugs to reduce inflammation and control the autoimmune response associated with lupus.
2. Use sunscreen
Protecting the skin from sun exposure by using sunscreen with a high SPF can help reduce the appearance of skin rashes and lupus flares.
3. Stress regulation
Stress management can help reduce lupus flares. Relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help calm the mind and body.
4. Food selection
Some people with lupus find that avoiding certain foods, such as foods high in saturated fat or foods containing gluten, can help reduce their symptoms. Consult a doctor or nutritionist to determine the right diet for lupus.
5. Regular physical activity
Regular physical exercise can help increase muscle strength, improve blood circulation, and improve heart health. However, it is important to choose the type of exercise that suits your physical condition and consult a doctor before starting a new exercise program.
6. Regular health monitoring
Continue to consult with the medical team for routine monitoring and evaluation of the lupus condition. These actions can help detect lupus flares early and treat other health problems that may arise.